Domestication has profoundly affected our canine companions. They have gone from carnivorous predators to pampered pets. Roughly 95% consider them members of their families. That’s huge for an animal we once considered a competitor. The gray wolf is the closest ancestor to the one these species diverged from 27,000 years ago.
Despite millennia of selective breeding, dogs remain facultative carnivores, benefiting most from a diet biased towards animal meat, fat, and by-products. As facultative carnivores though, dogs can indeed metabolize carbohydrates and starches, as you’d find in vegetables. Dogs can eat vegetables, although there are some notable exceptions.

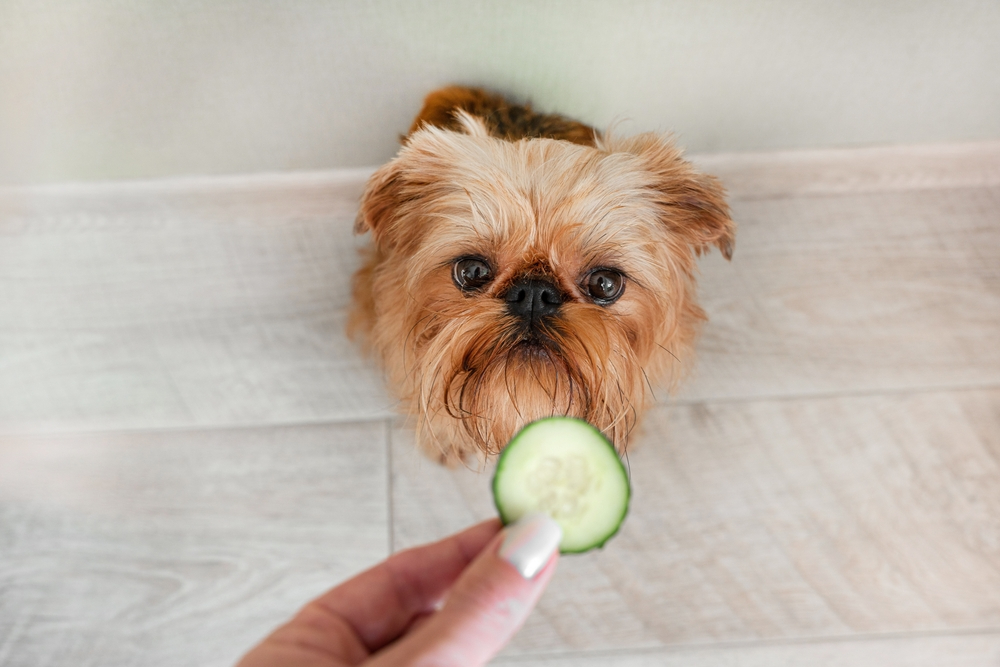
Why Dogs Can or Can’t Eat Vegetables
Digestibility is the overriding factor in deciding whether dogs can eat vegetables at all. Fundamentally, all macronutrients consumed by your dog – protein, fat, and carbohydrates, are eventually broken down to a simple sugar: glucose. Glucose remains the fundamental energy source that the various cells all over your dog’s body use for growth, repair, division, and function.
However, not all plant matter is the same just because they contain carbohydrates which can be broken down into said glucose. This phenomenon has been explored in research involving canines.1 In addition, dogs have poorer protein digestibility when fed diets containing plant matter compared to those with animal proteins.2
Dogs do process plant matter better than cats in many aspects, and have a lower protein requirement than cats do. However, they still do best on a diet of a carnivore rather than an omnivore and have a natural instinctive affinity for animal based foods over plant based options.3
Dogs can eat some vegetables. Homemade diets often use some vegetables to balance diets for dogs, but these are often in lower quantities than animal meats and organs in the diet. The other concerns with vegetables rest with the toxicity of some varieties. Sometimes, what is safe for us to consume can be toxic or even lethal for your pup.


Benefits and Dangers of Feeding Vegetables to Dogs
Whether or not dogs can eat vegetables isn’t always clear like how it is with chocolate (a big no-no for dogs). Meanwhile, vegetables can fall into good, okay, and bad categories. One of their benefits is fiber and the other nutrients they provide. Carrots, for example, are an excellent addition to your pup’s diet as a low-calorie treat. They are high in vitamin A and potassium. You’ll even see them in commercial dog foods.
Other safe vegetables include the following:
- Green beans
- Zucchini
- Cucumber
- Celery
- Bell peppers
- Broccoli
- Pumpkin
We recommend getting advice from a veterinarian if you have any questions or concerns regarding adding any vegetables to your dog’s diet.
💛 🐶 Speak To a Vet Online From the Comfort of Your Couch!


If you need to speak with a vet but can’t get to one, head over to PangoVet. It’s an online service where you can talk to a vet online and get the personalized advice you need for your pet — all at an affordable price!
The Dangers of Some Vegetables
Other vegetables are non-toxic to dogs but might cause digestive issues. Almost all plants found in any grocery store or market naturally contain cellulose. However, dogs (and even cats) cannot produce the enzyme cellulase, which helps break down cellulose into glucose. As such, caution is advised when feeding a dog any raw vegetables, as these may cause an upset stomach (even if they are not toxic for the dog).
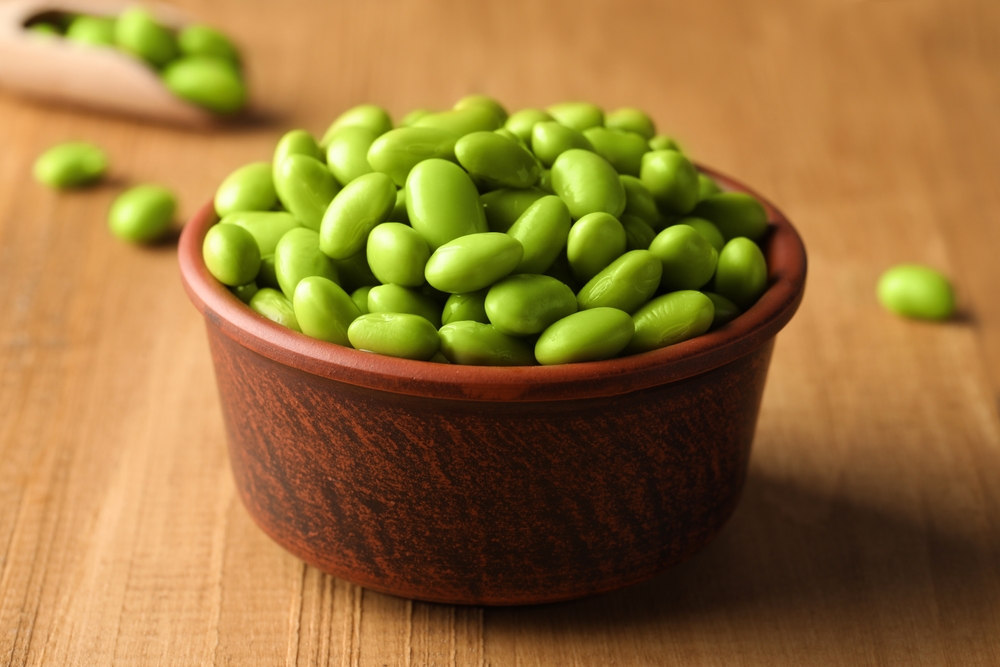


High-Oxalate Foods
Oxalic acid is present in many plants. The issue with this chemical compound involves its effect on magnesium and calcium in your dog’s body. It can bind with these minerals, leading to low blood levels. The reaction can also cause the formation of urinary stones. The vegetables you should avoid giving your dog in high amounts include spinach, beets, and edamame because of their high content.
Onions, Garlic, Chives, and Leeks
These Allium plants are all poisonous to dogs and cats and should never be given to pets in any quantity. While most of us can eat them without issues, it’s another matter for our companion animals. The problem rests with the sulfur-containing compounds that give them their characteristic smell. When your pet eats them, it causes hemolysis or the breakdown of red blood cells.
It doesn’t matter how they’re prepared. The reaction is the same, with the onset of signs within 24 or more hours after ingestion. A dog doesn’t have to eat a lot before this specific type of anemia occurs. Only 15 to 30 grams per kilogram of body weight can start the destruction of oxygen-carrying red blood cells.
Sadly, an antidote doesn’t exist. Treatment involves supportive care, including IV fluids, blood transfusions, and oxygen therapy. The prognosis depends on how early it’s caught.
Signs of accidental poisoning include the following:
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- GI distress
It’s worth noting that concentrated forms like powders and dehydrated flakes are more toxic than fresh vegetables. Nevertheless, the outcome is the same.


Tips for Giving Your Dog Vegetables
Our sobering account of onions is necessary because of the severity of consumption. Vegetables can be a welcome addition to your dog’s diet. However, they still are best as treats and shouldn’t make up more than 10% of your pet’s diet. It’s not that they’re bad for your dog; it’s just that they aren’t nutritionally complete.
Therefore, you can offer your dog the safe vegetables we discussed occasionally in small portions to avoid choking hazards. We recommend only giving your pet one kind at a time and monitoring their reaction to the new food. Make sure they are unseasoned and unsalted.

Conclusion
Dogs can eat many vegetables without ill effects. You’ll find many ingredients in commercial dog foods because of their nutritional value. We recommend giving fresh veggies to your dog sparingly as an occasional treat. Cooked and unseasoned items are best to offer and should be cut into small pieces.
Vegetables can provide an excellent low-calorie addition to your pup’s diet, but it’s best to make sure that they are eating a complete and balanced diet as their primary food source. For dogs on a homemade diet, the inclusion of vegetables is something you should consult with your veterinary nutritionist.
Featured Image Credit: ephotoshot, Shutterstock

