One of the rare parrot species that has successfully adapted to live in disturbed environments is the rose-ringed parakeet (Psittacula krameri). Escaped birds, which are a popular pet species, have taken over several towns worldwide, especially those in Northern and Western Europe.
These parakeets can withstand the chilly winters in Northern Europe and can thrive in a range of settings outside of their natural habitat. Although there is no threat to the species, its numbers have decreased in some areas of its natural habitat due to its appeal as a pet and disdain for farmers.
ROSE-RINGED PARAKEET
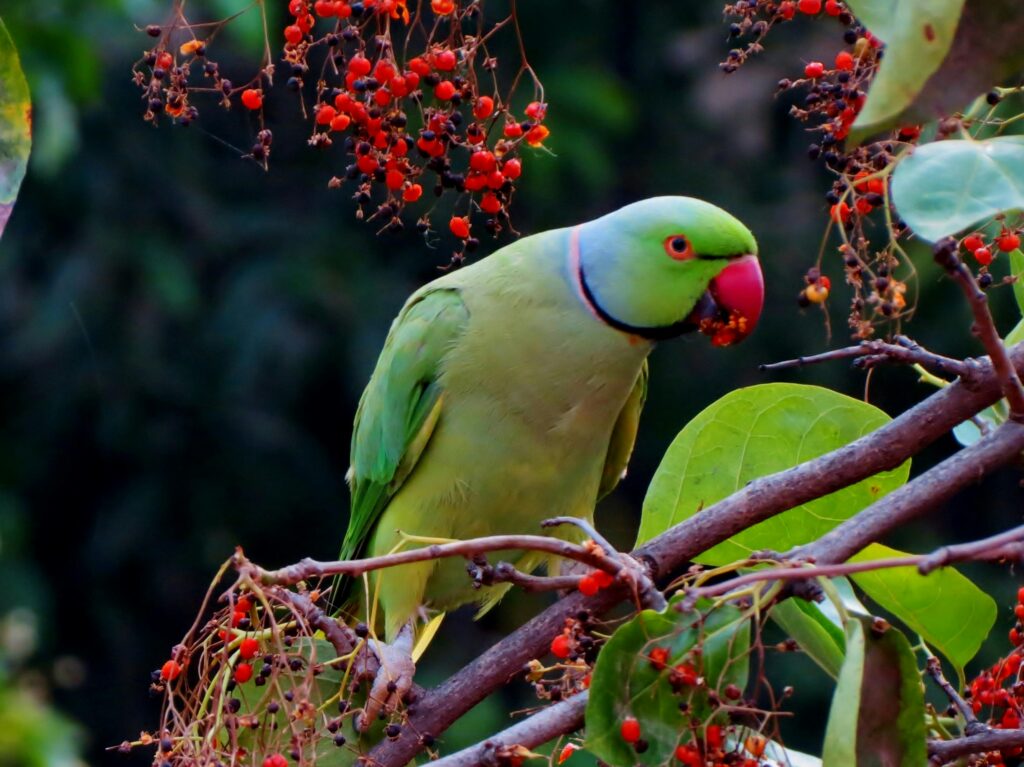

Appearance
A medium-sized parrot is the Rose-ringed parakeet. The hen and young birds of both sexes either have no neck rings at all or have neck rings that are shadow-like and pale to dark grey. The adult male bird has a neck ring that is both black and red. In the wild, both sexes are recognizable by their green hue, although captive-bred ringnecks can have a variety of colors, including blue, violet, and yellow.
Native Town
Africa and South Asia are the natural habitats of rose-ringed parakeets. They inhabit a broad range of environments and do not move. Grasslands, savannas, shrublands, rainforests, mangroves, and wetlands are among their habitats. These birds can also be found in agricultural and rural gardens.
Advice
Responsible Ownership: Avoid releasing captive parakeets into the wild.
Protect Crops: Farmers can use non-lethal methods to deter birds from damaging crops.
Education: Raise awareness about bird behavior and conservation.
Reporting: Report invasive sightings to wildlife authorities.
Habits and Lifestyle
Birds with rose-ringed parakeets are gregarious. They are busy during the day, spending their time flying around, foraging, and napping in the midday shade of trees. To forage on farms and orchards, they frequently congregate in flocks and fly many kilometers together. Rose-ringed parakeets have a distinctive squawking cry that makes them quite loud.

Nutrition and Diet
As herbivores, rose-ringed parakeets often consume buds, fruits, vegetables, nuts, berries, and seeds. In India, they consume cereal grains as well as pigeon peas in the winter. They graze on mulberries in the spring and dates in the summer, as well as crops like maize and sunflowers.
Diet
- Herbivore
- Granivore
- Frugivore
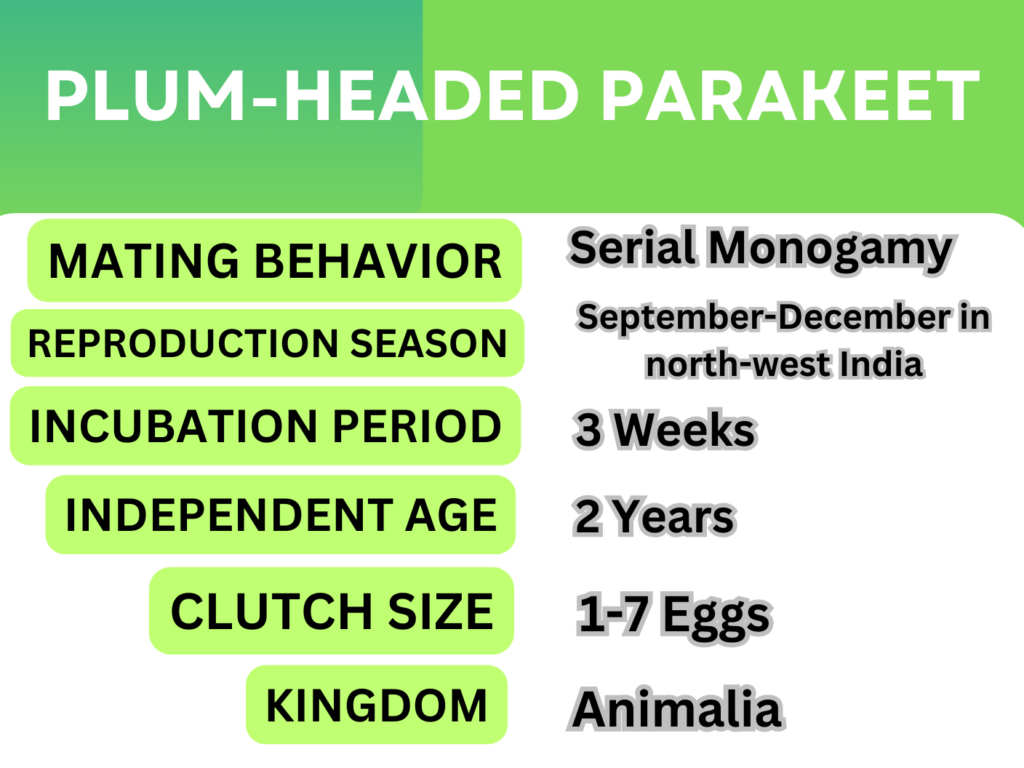
Habits of Mating
Rose-ringed parakeets are serial monogamous, meaning they frequently mate with another individual during the next breeding season; they do not have life partners. Rose-ringed parakeets form couples in northwest India from September to December.
They choose and protect their nesting locations during this cold season to prevent competition from other birds for these locations. For around three weeks, the female lays one to seven eggs and incubates them by herself. Because they hatch altricial, the chicks are defenseless and rely on their parents for sustenance and protection. At seven weeks of age, the young fledge, and at two years old, they gain independence. Around age three, a child typically reaches reproductive maturity.
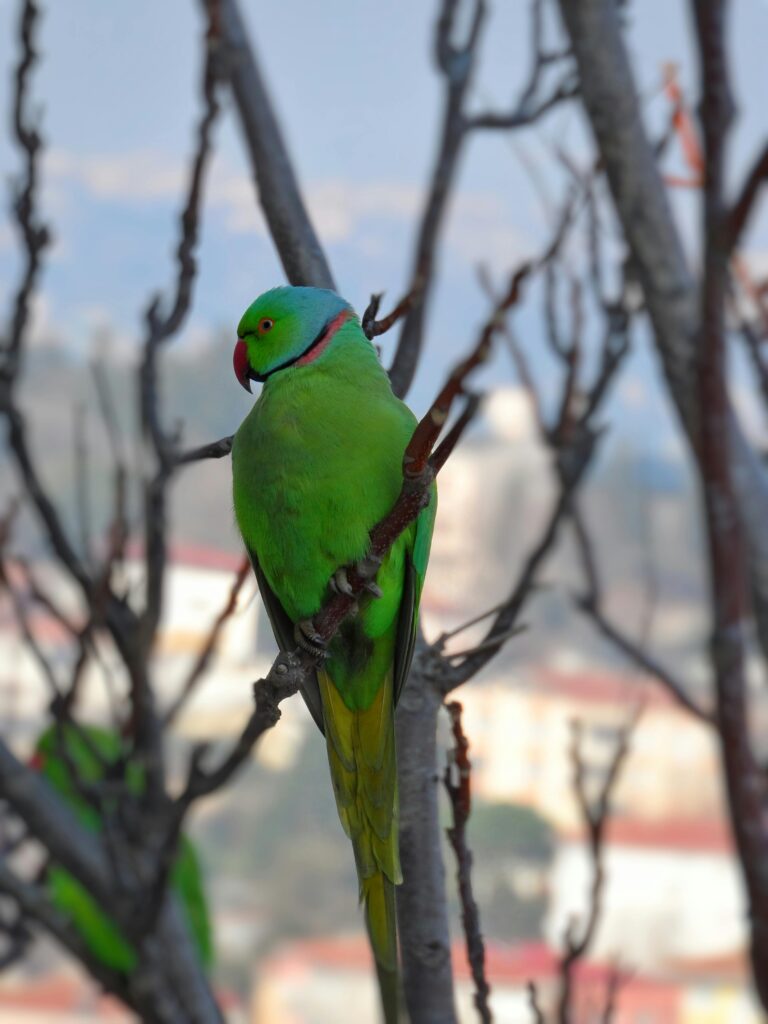

Population
Population threats
The Rose-ringed parakeet’s population seems to be growing, however in some areas of its natural habitat, its numbers have decreased due to its appeal as a pet and disfavor among farmers.
Total population
The Rose-ringed parakeet is abundant and widespread across its habitat, according to the IUCN, however an estimate of its total population is unknown. On the other hand, estimates of its numbers in Japan place the number of invasive breeding pairs at between 100,000 and 100,000. According to the IUCN Red List, the rose-ringed parakeet is now classed as Least Concern (LC), and its population is growing.
Facts
- Rose-ringed parakeets kept in captivity can be trained to talk. It is also possible for men and females to mimic human speech. The bird mimics the human speaker’s speech after first listening to its surroundings. For this reason, some nurture Rose-ringed parakeet chicks by hand. After that, these parrots become quite calm and open to education.
- Rose-ringed parakeets have a long history in aviculture and are popular pets. Additionally, these birds have been released into a variety of cities throughout the globe, where they may get their favorite food sources—seeds, nuts, fruits, and berries—from residential gardens and bird feeders in a habitat devoid of predators. These parakeets can readily survive European winter temperatures because of their adaptations to the harsh winters in the foothills of the Himalayas.
- Rose-ringed parakeets are regarded as major pests by farmers because they frequently destroy farmlands and orchards. Farmers are not delighted with these birds.

Behavioral Adaptations
Rose-ringed parakeets exhibit remarkable behavioral adaptations to urban environments. They have been observed nesting in artificial structures such as electrical pylons and buildings, showcasing their ability to adapt to human-altered landscapes.
Social Structure
Within their flocks, rose-ringed parakeets display complex social behaviors. They form strong pair bonds during the breeding season and engage in cooperative behaviors such as communal roosting and feeding, which may contribute to their success in colonizing new areas.
Conservation Efforts
While the species is classified as Least Concern by the IUCN due to its overall population stability, localized declines in some areas underscore the importance of conservation efforts. Initiatives such as habitat restoration and public awareness campaigns can help mitigate human-wildlife conflicts and promote coexistence.
Conclusion
The rose-ringed parakeet, with its remarkable adaptability and widespread distribution, presents both opportunities and challenges for humans and ecosystems alike. While its success in urban environments and popularity as a pet species are notable, it’s crucial to approach interactions with these birds thoughtfully to ensure the well-being of both the species and its surrounding environment.
By promoting responsible ownership, implementing measures to mitigate agricultural damage, fostering public education, and monitoring invasive populations, we can strive for a harmonious coexistence with these colorful and charismatic birds.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are rose-ringed parakeets harmful to native bird species?
While they can compete with native birds for resources in some areas, the impact varies depending on the specific ecosystem and management practices.
Can I keep a rose-ringed parakeet as a pet?
Yes, but it’s essential to adopt from reputable sources and provide appropriate care to ensure the bird’s well-being. Avoid releasing captive parakeets into the wild.
How can farmers protect their crops from rose-ringed parakeets?
Farmers can use non-lethal methods such as netting, reflective tape, or scare devices to deter birds from damaging crops.
Are rose-ringed parakeets endangered?
No, they are classified as Least Concern by the IUCN, but localized declines in some areas emphasize the importance of conservation efforts.
What should I do if I spot an invasive population of rose-ringed parakeets?
Report sightings to local wildlife authorities or citizen science initiatives to aid in monitoring and management efforts.
Do rose-ringed parakeets have any unique behaviors?
Yes, they exhibit complex social behaviors within their flocks and demonstrate remarkable adaptability to urban environments.
Can rose-ringed parakeets mimic human speech?
Yes, captive parakeets can be trained to mimic human speech, showcasing their intelligence and ability to learn.
